Temporal relation extraction with a graph-based deep biaffine attention model
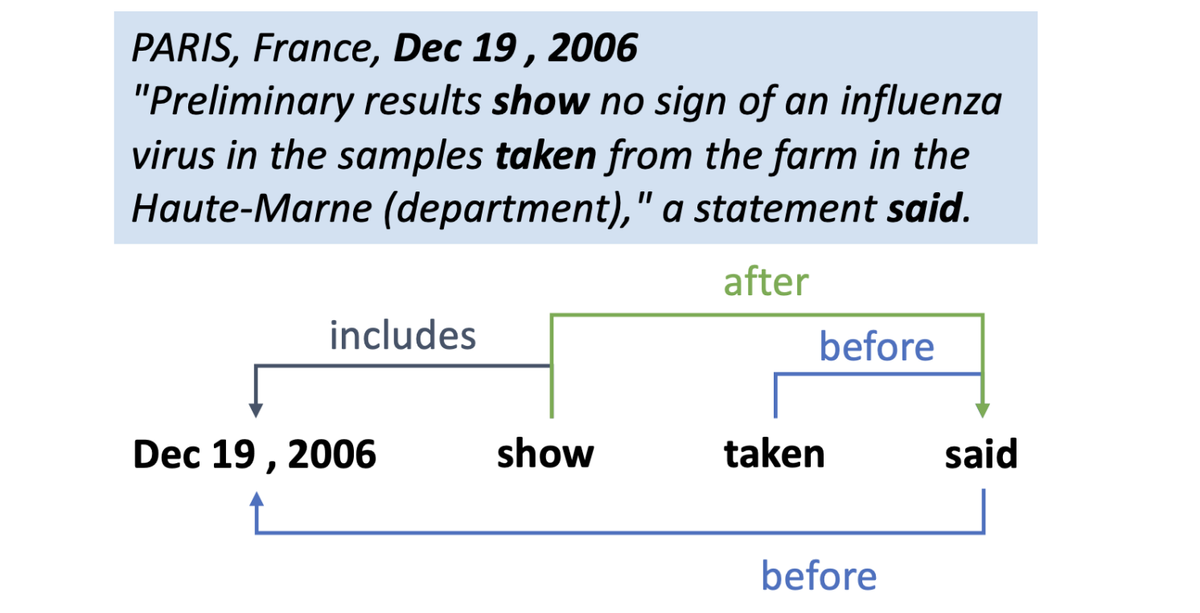
Our recent research focuses on improving temporal relation extraction from unstructured text. We've developed a novel model that not only employs deep learning techniques but also integrates temporal logic for more effective relation extraction. This approach addresses the limitations of traditional models by generating a synthetic dataset, which is then used in conjunction with dependency parsers. This method improves the model's ability to learn and understand complex temporal relationships in text.
visit our detailed project report:
link
pdf
Approach
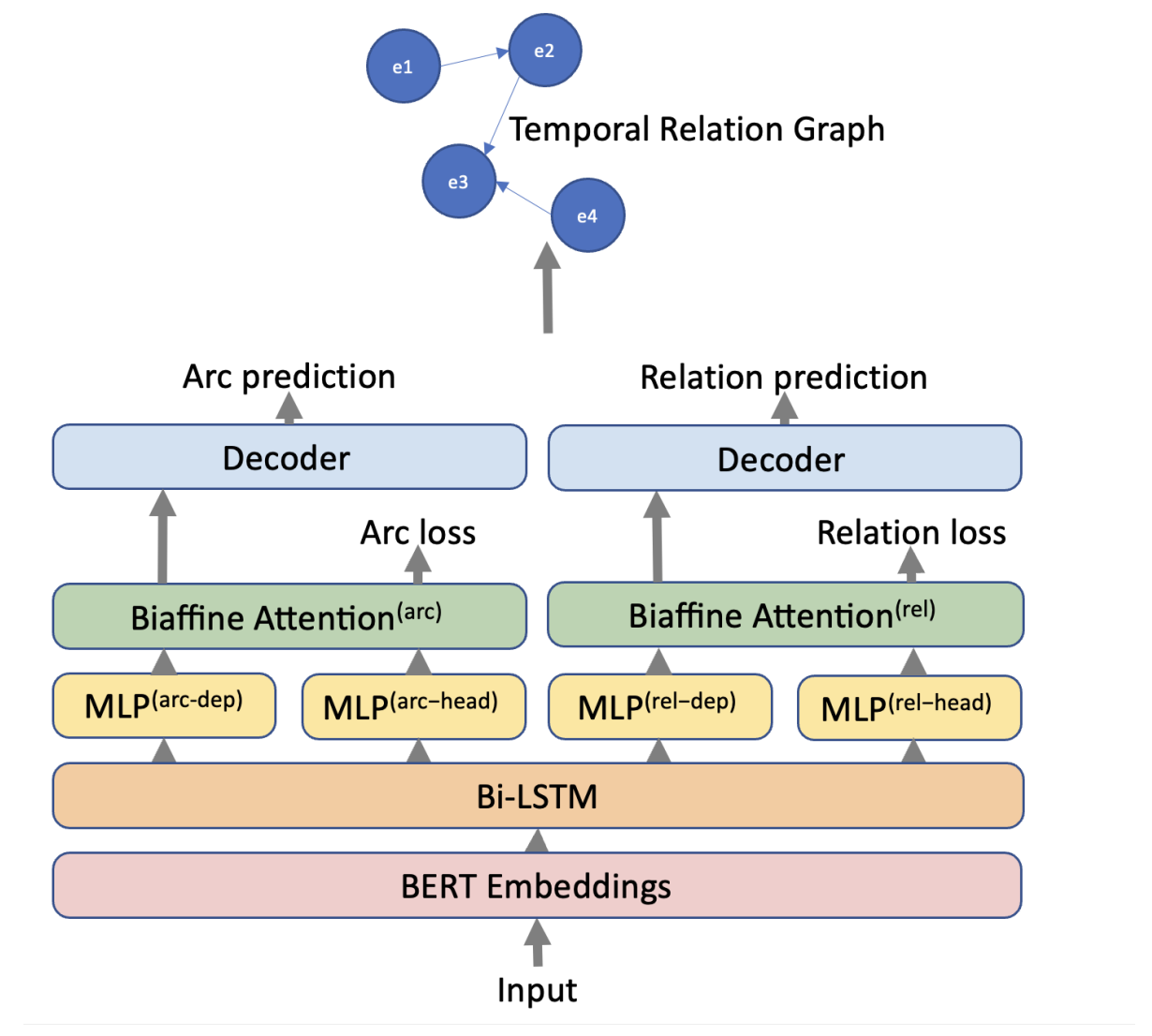
Our approach utilizes a layered architecture to extract temporal relations from text. At the base, we have BERT embeddings that capture contextual information from the input. These feed into a Bi-LSTM layer that adds sequential understanding. For specific relation extraction, we use a biaffine attention mechanism with Multilayer Perceptrons (MLPs) to focus on the dependency (arc) and the type of relationship (relation) between events. This structure enables precise predictions of temporal relations, forming a graph that represents the interconnectedness of events within the text.
Achieveing SOTA accuracy while processing more sentence/second
Benchmarks show that in a fixed amount of time, our model processes more sentences that previous studies, while providing comparable accuracy. This is primary due to our model design that removes the event extraction dependency for relation extraction. The prediction of temporal relation labels is performed in parallel with arc prediction, eliminating the need of the non-parallelizable, nested for-loop for extracting event pairs in the previous studies.
Why this work may be useful
This work is useful because it exploits the logical structure of temporal relation tasks. By aligning with temporal logic principles and employing sophisticated language models, it has the potential to surpass current performance benchmarks in understanding textual timelines. This has potential in advancing applications in areas that require detailed, precise comprehension of events over long time horizon.
Why this work may not be useful
The work may be less impactful in certain contexts, particularly in light of the advances made by large language models. These LLMs have demonstrated superior accuracy in temporal relation tasks and are adept at recognizing even subtle and obscure events. This capability stems from their extensive training on diverse datasets, enabling them to understand and predict complex temporal patterns. Consequently, specialized approaches like the one in question might not offer additional benefits over these highly efficient, generalized models in certain applications.
Vertdict: Might be useful in the future given significant breakthough in Neuro-symbolic AI